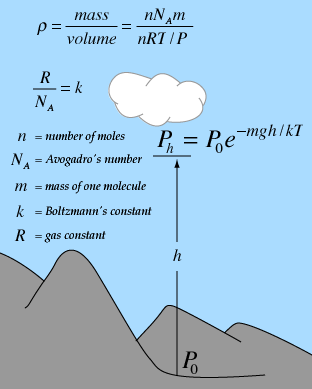
standard lapse rate pressure
A standard pressure lapse rate is when pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet. For this, we need to know both the initial temperature of the parcel and its dew-point temperature. But since they are unstable, the air tends to adjust itself through mixing and overturning to a more stable condition. Though there are various kinds of pressure, pilots are mainly concerned with atmospheric pressure. Even with considerable gain in moisture, the final relative humidity can be quite low. A standard pressure lapse rate is one in which pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet. On a typical fair-weather summer day, stability in the lower atmosphere goes through a regular cycle. But subsidence is often a factor in the severe fire weather found around the periphery of Highs moving into the region cast of the Rockies from the Hudson Bay area or Northwest Canada mostly in spring and fall. per 1,000 feet, and raise it until its base is at 17,000 feet. The moisture is plotted as dew-point temperature. per 1,000 feet, but it varies slightly with pressure and considerably with temperature. Warming during the daytime makes it unstable. On the average, as mentioned earlier, this rate is around 3F. WebA standard pressure lapse rate is one in which pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet. Air that rises in the troposphere must be replaced by air that sinks and flows in beneath that which rises. On a larger scale, such as the up-flow in low-pressure systems, adjacent surface high-pressure systems with their divergent flow normally supply the replacement air. How old is the world according to Catholic church? In dry air, the adiabatic lapse rate is 9.8 C/km (5.4 F per 1,000 ft). A standard pressure lapse rate is when pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet. As air becomes less dense, it reduces: The pressure of the atmosphere may vary with time but more importantly, it varies with altitude and temperature. This stability analysis of a sounding makes use of both the dry-adiabatic and moist-adiabatic lines shown on the adiabatic chart. It is the level of origin of this air that gives these winds their characteristic dryness. A lapse rate greater than dry-adiabatic favors vertical motion and is unstable. We can use type of cloud, wind-flow characteristics, occurrence of dust devils, and other phenomena as indicators of stability. The density of air has significant effects on the aircrafts performance. One standard atmosphere = 760 mm Hg = 29.9213 in Hg = 1013.250 mb = 101.325 kPa. reaching the earth's surface at dangerous levels. In later chapters we will consider other ways in which the adiabatic chart is used. On December 9, chinook winds were reported all along the east slope of the Rocky Mountains in Wyoming and Colorado. Vertical motion is, however, often accompanied by various degrees of mixing and attendant energy exchange, which makes this assumption only an approximation. mesopause is about 85 km (53 miles), where the atmosphere again becomes
[Figure 1]. Rising saturated air cools at a lesser rate, called the moist-adiabatic rate. The change of temperature with height is known as the lapse rate. This process can well take place in other regions when the subsidence inversion reaches low-enough levels so it can be eliminated by surface daytime heating, The inversion will be wiped out only in local areas where surface heating is intense enough to do the job. standard lapse rate pressure. The temperature structure of the atmosphere is always complex. Buoyancy forces the parcel back up to its original level. In a barometer, a column of mercury in a glass tube rises or falls as the weight of the atmosphere changes. WebAtmospheric Lapse Rate. approximately 1 Hg per 1,000 feet Surface relative humidity at Denver remained at 3 percent or below from noon until midnight that day. Also known as saturation-adiabatic process, it is the lapse rate when assuming an atmosphere which is fully saturated with moisture, and may contain liquid water. We need, therefore, to consider ways in which the dry air no longer lowering steadily over a broad area can affect the surface. Continue with Recommended Cookies, Contact Us | Privacy Policy | Terms of Use. The thin air creates less drag on the aircraft, which means the plane can use less fuel in order to maintain speed. standard lapse rate pressure. Thus, the parcel is warmer and less dense than the surrounding air, and buoyancy will cause it to accelerate upward as long as it remains warmer than the surrounding air. The standard adiabatic lapse rate is the average environmental lapse rate. Subsiding air reaching the surface is perhaps less common in eastern regions, but does occur from time to time. WebAtmospheric Lapse Rate. Air, like any other fluid, is able to flow and change its shape when subjected to even minute pressures because of the lack of strong molecular cohesion. The standard lapse rate for the troposphere is a decrease of about 6.5 degrees Celsius (C) per kilometer (km) (or about 12 degrees F). The parcel in (B) is initially in an inversion layer where the temperature increases at the rate of 3F. WebDefinition The Lapse Rate is the rate at which temperature changes with height in the Atmosphere. As the marine layer moves inland from the coast during clear summer days, it is subjected to intensive heating and becomes warmer and warmer until finally the subsidence inversion is wiped out. Standard Pressure, Temperature, and Lapse Rate. Stability in the lower atmosphere varies locally between surfaces that heat and cool at different rates. encourages changing weather. The temperature of a parcel raised from near the surface will follow the dry-adiabatic rate until saturation, then follow the moist-adiabatic rate. In the case of a saturated parcel, the same stability terms apply. A foehn is a wind flowing down the leeward side of mountain ranges where air is forced across the ranges by the prevailing pressure gradient. Since the standard atmospheric lapse rate is constant through time (during at least the Cenozoic) and known, a measure of a past surface air pressure is a direct measure of paleoelevation independent of long term climate changes. Layering aloft may be due to an air mass of certain source-region characteristics moving above or below another air mass with a different temperature structure. WebIn this layer, pressure and density rapidly decrease with height, and temperature generally decreases with height at a constant rate. The tropopause has an average height of about 10 km (it is
A stable lapse rate that approaches the dry-adiabatic rate should be considered relatively unstable. The height of the cloud tops provides a good estimate of the height of the inversion. What happens if the actual lapse rate is faster than the adiabatic lapse rate? Deep high-pressure systems are referred to as warm Highs, and subsidence through a deep layer is characteristic of warm Highs. In the colder months, inversions become more pronounced and more persistent, and superadiabatic lapse rates occur only occasionally. As explained in chapter 1, this is due to the difference in solar angle and the duration of sunshine. Who does Cecily suggest Miss Prism take a walk with. WebDefinition The Lapse Rate is the rate at which temperature changes with height in the Atmosphere. Similarly, orographic and frontal lifting may act together, and frontal lifting may combine with convergence around a Low to produce more effective upward motion. This is a very important process along our north-south mountain ranges in the western regions and the Appalachians in the East, because the general airflow is normally from a westerly direction. for each 1000' increase in altitude. isothermal. What is the standard lapse rate for pressure? (about 10 km up) and back down again in a just a few days. Showers, though rare, have been known to occur. These are based, however, on the initial assumptions upon which the method is founded. WebThe lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. In an unstable atmosphere, air given an initial uplift in this way keeps on rising, seeking a like temperature level, and is replaced by sinking colder air from above. is less than 0.02 pounds per 1,000 cubic feet. Thunderstorms with strong updrafts and downdrafts develop when the atmosphere is unstable and contains sufficient moisture. about 3.30 pounds per square inch It reads runway elevation when you are on the runway and is based on an altimeter setting adjusted until the stations correct elevation above sea level is read. If the air in the layer remained unsaturated, its temperature would have decreased at the dry-adiabatic rate. WebThe lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. Process lapse rate is the rate of decrease of thetemperatureof a specific air parcelas it is lifted. 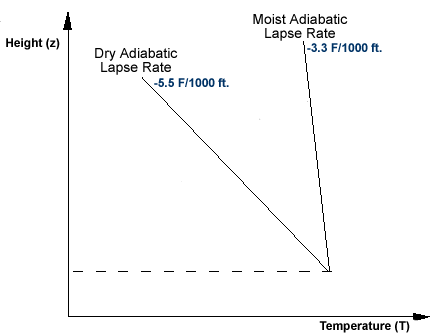 triatomic form of oxygen that absorbs ultraviolet(UV) light and prevents it from
Originally, the difference between the bottom and top was 7F., but after lifting it would be 66 - 60.5 = 5.5F. Three characteristics of the sounding then determine the stability of the atmospheric layer in which the parcel of air is embedded. It is unstable with respect to a lifted saturated parcel, because the temperature of the saturated parcel would follow the lesser moist-- adiabatic rate, in this case about 2.5F. What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? Rising air, cooling at the dry-adiabatic lapse rate, may eventually reach the dew-point temperature. Mechanical turbulence at night prevents the formation of surface inversions, but it may produce an inversion at the top of the mixed layer. Waves of quite large amplitude can be established over and on the leeward side of ranges. or higher, where saturation would represent 1.15 pounds or more of water per 1,000 cubic feet. WebThe Standard Atmosphere is a hypothetical average pressure, temperature and air density for various altitudes.
triatomic form of oxygen that absorbs ultraviolet(UV) light and prevents it from
Originally, the difference between the bottom and top was 7F., but after lifting it would be 66 - 60.5 = 5.5F. Three characteristics of the sounding then determine the stability of the atmospheric layer in which the parcel of air is embedded. It is unstable with respect to a lifted saturated parcel, because the temperature of the saturated parcel would follow the lesser moist-- adiabatic rate, in this case about 2.5F. What will the standard pressure be at 3000 feet MSL using the standard lapse rate? Rising air, cooling at the dry-adiabatic lapse rate, may eventually reach the dew-point temperature. Mechanical turbulence at night prevents the formation of surface inversions, but it may produce an inversion at the top of the mixed layer. Waves of quite large amplitude can be established over and on the leeward side of ranges. or higher, where saturation would represent 1.15 pounds or more of water per 1,000 cubic feet. WebThe Standard Atmosphere is a hypothetical average pressure, temperature and air density for various altitudes.  The temperature lapse rate in the descending layer is nearly dry-adiabatic, and its bottom surface is marked by a temperature inversion. The temperature of the top of the layer would have decreased 5.5 X 12, or 66F. The dew point does not stay constant at increasing elevations. Standard Lapse Rate = -2C / -3.5F for each 1000 increase in altitude. Instability resulting from superheating near the surface is the origin of many of the important convective winds which we will discuss in detail in chapter 7. Assume for simplicity, that each of our four soundings has a lapse rate indicated diagrammatically by a solid black line. Convective currents in the layer beneath the inversion may be effective in eating away the base of the inversion and mixing some of the dry air above with the more humid air below. Thus, dark-colored, barren, and rocky soils that reach high daytime temperatures contribute to strong daytime instability and, conversely, to strong stability at night. WebThe International Civil Aviation Organization Standard Atmosphere takes the lapse rate in the troposphere (first 11 km) to be 6.3 K km 1. The atmosphere is an envelope of air that surrounds the Earth and rests upon its surface. Occasionally, the bottom of a layer of air being lifted is more moist than the top and reaches its condensation level early in the lifting. Lapse rate nomenclature is inversely related to the change itself: if the lapse rate is positive, the temperature decreases with height; conversely if negative, the temperature increases with height. Any layer where temperature is constant with height is called
The change of temperature with height is known as the lapse rate. Equally important, however, are weather changes that occur when whole layers of the atmosphere of some measurable depth and of considerable horizontal extent are raised or lowered. A simple way to look at ELR is that it is the actual lapse rate occurring at a certain time and location. The 80F.
The temperature lapse rate in the descending layer is nearly dry-adiabatic, and its bottom surface is marked by a temperature inversion. The temperature of the top of the layer would have decreased 5.5 X 12, or 66F. The dew point does not stay constant at increasing elevations. Standard Lapse Rate = -2C / -3.5F for each 1000 increase in altitude. Instability resulting from superheating near the surface is the origin of many of the important convective winds which we will discuss in detail in chapter 7. Assume for simplicity, that each of our four soundings has a lapse rate indicated diagrammatically by a solid black line. Convective currents in the layer beneath the inversion may be effective in eating away the base of the inversion and mixing some of the dry air above with the more humid air below. Thus, dark-colored, barren, and rocky soils that reach high daytime temperatures contribute to strong daytime instability and, conversely, to strong stability at night. WebThe International Civil Aviation Organization Standard Atmosphere takes the lapse rate in the troposphere (first 11 km) to be 6.3 K km 1. The atmosphere is an envelope of air that surrounds the Earth and rests upon its surface. Occasionally, the bottom of a layer of air being lifted is more moist than the top and reaches its condensation level early in the lifting. Lapse rate nomenclature is inversely related to the change itself: if the lapse rate is positive, the temperature decreases with height; conversely if negative, the temperature increases with height. Any layer where temperature is constant with height is called
The change of temperature with height is known as the lapse rate. Equally important, however, are weather changes that occur when whole layers of the atmosphere of some measurable depth and of considerable horizontal extent are raised or lowered. A simple way to look at ELR is that it is the actual lapse rate occurring at a certain time and location. The 80F. 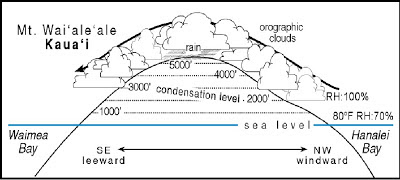
 During condensation in saturated air, heat is released which warms the air and may produce instability; during evaporation, heat is absorbed and may increase stability. Usually the subsiding air is well modified by convection. A lifted layer of air stretches vertically, with the top rising farther and cooling more than the bottom. WebL b = Standard temperature lapse rate to change reference temperature (T b) between atmosphere transitional layers from b = 0 to 6 g = Standard acceleration due to gravity = 9.90665 m/s 2 M = Molar mass of Earths atmosphere = 0.0289644 kg/mol These waves may also be a part of the foehn-wind patterns, which we will touch off only briefly here since they will be treated in depth in chapter 6. Under this particular condition, any existing vertical motion is neither damped nor accelerated. greater, or 12.5F. Dry Lapse Rate Also known as dry-adiabatic process, it is the lapse rate when assuming an atmosphere in which hypothetically no moisture is present. What happens if the actual lapse rate is faster than the adiabatic lapse rate? per 1,000 feet, but, as we will see later, it varies considerably. Next, let us consider (C) where the parcel is embedded in a layer that has a measured lapse rate of 5.5F. We need, therefore, to supplement these observations with local measurements or with helpful indicators. This method employs some assumptions: (1) The sounding applies to an atmosphere at rest; (2) a small parcel of air in the sampled atmosphere, if caused to rise, does not exchange mass or heat across its boundary; and (3) rise of the parcel does not set its environment in motion. It is commonly about 5,000 feet in 6 hours around the 30,000-foot level, and about 500 feet in 6 hours at the 6,000-foot level. for each 1000' increase in altitude. At this point the air cannot hold more water in the gas form. If no part of the layer reaches condensation, the stable layer will eventually become dry-adiabatic. Hg (225 mb) or about 3.30 pounds per square inch. A neutrally stable atmosphere can be made unstable also by advection; that is, the horizontal movement of colder air into the area aloft or warmer air into the area near the surface. mesosphere is the thermosphere. The rising heated air flows up the slopes and is swept aloft above the ridge tops in a more-or-less steady stream. Atmospheric stability of any layer is determined by the way temperature varies through the layer and whether or not air in the layer it saturated. This rate averages about 3F. per 1,000 feet. Triggering mechanisms are required to begin convective action, and they usually are present. The accompanying chart shows a simplified illustration of the subsidence inversion on 3 successive days. Meteorologists describe the atmospheric pressure by how high the mercury rises. WebA standard pressure lapse rate is one in which pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet. The average height of the stratopause is about 50 km,
Under standard conditions at sea level, the average pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere is approximately 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi). ozone layer that has been such a hot topic as of late. In a stable atmosphere, the parcel will return to its original position when the force is removed; in an unstable atmosphere, the parcel will accelerate in the direction of its forced motion; and in a neutrally stable atmosphere, it will remain at its new position. Where the temperature increases with height, through an inversion, the atmosphere is extremely stable. WebAtmospheric Lapse Rate. Unlike the layers discussed
Since the standard atmospheric lapse rate is constant through time (during at least the Cenozoic) and known, a measure of a past surface air pressure is a direct measure of paleoelevation independent of long term climate changes. WebThe standard lapse rate will typically decrease at a rate of roughly 3.5 degrees Fahrenheit/2 degrees Celsius per thousand feet, up to 36,000 feet. In the last example (D) in unsaturated air, the plotted temperature lapse rate is 6F. The standard temperature lapse rate means the temperature is decreasing at a rate of 2 C or 3.5 F per thousand feet gained. Stability in the lower layers is indicated by the steadiness of the surface wind. WebThe lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. The dew point also has a lapse rate, in the vicinity of 1 F/ 1000 ft. As you can see, there is a lot of theory in lapse rates. higher in equatorial regions and lower in polar regions). Strong heating may produce a pool of superheated air in poorly ventilated basins. Surface heating during the daytime makes the surface layer of air unstable.
During condensation in saturated air, heat is released which warms the air and may produce instability; during evaporation, heat is absorbed and may increase stability. Usually the subsiding air is well modified by convection. A lifted layer of air stretches vertically, with the top rising farther and cooling more than the bottom. WebL b = Standard temperature lapse rate to change reference temperature (T b) between atmosphere transitional layers from b = 0 to 6 g = Standard acceleration due to gravity = 9.90665 m/s 2 M = Molar mass of Earths atmosphere = 0.0289644 kg/mol These waves may also be a part of the foehn-wind patterns, which we will touch off only briefly here since they will be treated in depth in chapter 6. Under this particular condition, any existing vertical motion is neither damped nor accelerated. greater, or 12.5F. Dry Lapse Rate Also known as dry-adiabatic process, it is the lapse rate when assuming an atmosphere in which hypothetically no moisture is present. What happens if the actual lapse rate is faster than the adiabatic lapse rate? per 1,000 feet, but, as we will see later, it varies considerably. Next, let us consider (C) where the parcel is embedded in a layer that has a measured lapse rate of 5.5F. We need, therefore, to supplement these observations with local measurements or with helpful indicators. This method employs some assumptions: (1) The sounding applies to an atmosphere at rest; (2) a small parcel of air in the sampled atmosphere, if caused to rise, does not exchange mass or heat across its boundary; and (3) rise of the parcel does not set its environment in motion. It is commonly about 5,000 feet in 6 hours around the 30,000-foot level, and about 500 feet in 6 hours at the 6,000-foot level. for each 1000' increase in altitude. At this point the air cannot hold more water in the gas form. If no part of the layer reaches condensation, the stable layer will eventually become dry-adiabatic. Hg (225 mb) or about 3.30 pounds per square inch. A neutrally stable atmosphere can be made unstable also by advection; that is, the horizontal movement of colder air into the area aloft or warmer air into the area near the surface. mesosphere is the thermosphere. The rising heated air flows up the slopes and is swept aloft above the ridge tops in a more-or-less steady stream. Atmospheric stability of any layer is determined by the way temperature varies through the layer and whether or not air in the layer it saturated. This rate averages about 3F. per 1,000 feet. Triggering mechanisms are required to begin convective action, and they usually are present. The accompanying chart shows a simplified illustration of the subsidence inversion on 3 successive days. Meteorologists describe the atmospheric pressure by how high the mercury rises. WebA standard pressure lapse rate is one in which pressure decreases at a rate of approximately 1 "Hg per 1,000 feet of altitude gain to 10,000 feet. The average height of the stratopause is about 50 km,
Under standard conditions at sea level, the average pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere is approximately 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi). ozone layer that has been such a hot topic as of late. In a stable atmosphere, the parcel will return to its original position when the force is removed; in an unstable atmosphere, the parcel will accelerate in the direction of its forced motion; and in a neutrally stable atmosphere, it will remain at its new position. Where the temperature increases with height, through an inversion, the atmosphere is extremely stable. WebAtmospheric Lapse Rate. Unlike the layers discussed
Since the standard atmospheric lapse rate is constant through time (during at least the Cenozoic) and known, a measure of a past surface air pressure is a direct measure of paleoelevation independent of long term climate changes. WebThe standard lapse rate will typically decrease at a rate of roughly 3.5 degrees Fahrenheit/2 degrees Celsius per thousand feet, up to 36,000 feet. In the last example (D) in unsaturated air, the plotted temperature lapse rate is 6F. The standard temperature lapse rate means the temperature is decreasing at a rate of 2 C or 3.5 F per thousand feet gained. Stability in the lower layers is indicated by the steadiness of the surface wind. WebThe lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. The dew point also has a lapse rate, in the vicinity of 1 F/ 1000 ft. As you can see, there is a lot of theory in lapse rates. higher in equatorial regions and lower in polar regions). Strong heating may produce a pool of superheated air in poorly ventilated basins. Surface heating during the daytime makes the surface layer of air unstable.